There are following 4 basic types of flip flops-
- SR Flip Flop
- JK Flip Flop
- D Flip Flop
- T Flip Flop
In this article, we will discuss about JK Flip Flop.
JK Flip Flop-
| JK flip flop is a refined & improved version of SR Flip Flop that has been introduced to solve the problem of indeterminate state that occurs in SR flip flop when both the inputs are 1. |
In JK flip flop,
- Input J behaves like input S of SR flip flop which was meant to set the flip flop.
- Input K behaves like input R of SR flip flop which was meant to reset the flip flop.
Construction of JK Flip Flop-
There are following two methods for constructing a JK flip flop-
- By using SR flip flop constructed from NOR latch
- By using SR flip flop constructed from NAND latch
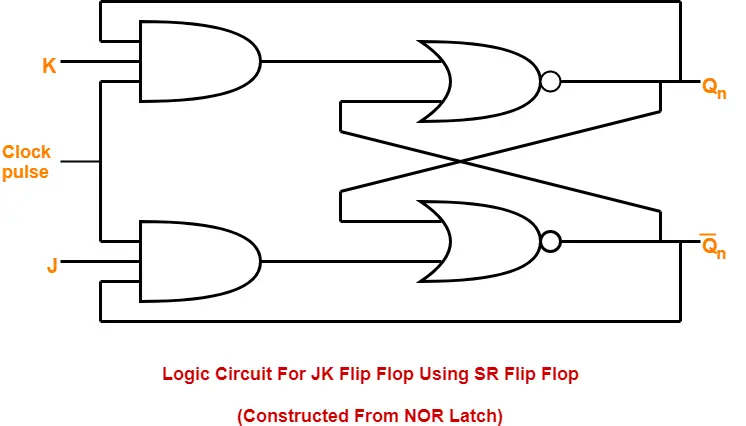
1. Construction of JK Flip Flop By Using SR Flip Flop Constructed From NOR Latch-
This method of constructing JK Flip Flop uses-
- SR Flip Flop constructed from NOR latch
- Two other connections
Logic Circuit-
The logic circuit for JK Flip Flop constructed using SR Flip Flop constructed from NOR latch is as shown below-
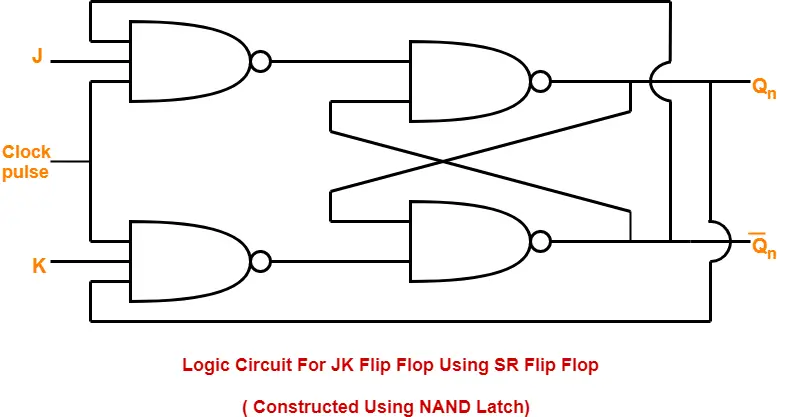
2. Construction of JK Flip Flop By Using SR Flip Flop Constructed From NAND Latch-
This method of constructing JK Flip Flop uses-
SR Flip Flop constructed from NAND latch
- Two other connections
Logic Circuit-
The logic circuit for JK Flip Flop constructed using SR Flip Flop constructed from NAND latch is as shown below-
Logic Symbol-
The logic symbol for JK Flip Flop is as shown below-

Truth Table-
The truth table for JK Flip Flop is as shown below-
| INPUTS | OUTPUTS | ||
| J | K | Qn (Present State) | Qn+1 (Next State) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Truth Table
The above truth table may be reduced as-
| INPUTS | OUTPUTS | REMARKS | ||
| J | K | Qn (Present State) | Qn+1 (Next State) | States and Conditions |
| 0 | 0 | X | Qn | Hold State condition J = K = 0 |
| 0 | 1 | X | 0 | Reset state condition J = 0 , K = 1 |
| 1 | 0 | X | 1 | Set state condition J = 1 , K = 0 |
| 1 | 1 | X | Q’n | Toggle state condition J = K = 1 |
Truth Table
Characteristic Equation-
Draw a k map using the above truth table-
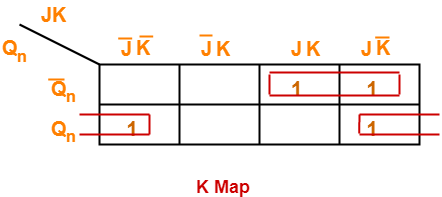
From here-
Qn+1 = Q’n (JK + JK’) + Qn (J’K’ + JK’)
| Qn+1 = Q’nJ + QnK’ |
Excitation Table-
The excitation table of any flip flop is drawn using its truth table.
| Qn | Qn+1 | S | R |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | X |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | X |
| 1 | 0 | X | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | X | 0 |
Excitation Table
SR Flip Flop Vs JK Flip Flop-
Both JK flip flop and SR flip flop are functionally same.
The only difference between them is-
- In JK flip flop, indeterminate state does not occur.
- In JK flip flop, instead of indeterminate state, the present state toggles.
- In other words, the present state gets inverted when both the inputs are 1.
To gain better understanding about JK Flip Flop,

